Configure QUANTEEC for eCDN usage
The QUANTEEC plugin can be used to optimize the performance of video distribution within a company, known as an eCDN (enterprise Content Delivery Network). In your QUANTEEC customer area, you can set up one or more eCDN configurations to suit your needs.
Configure sites and eCDN rules
In the Panel
In the next session of the page called List of sites, you can create specific P2P rules for global use cases, sites, and/or subdomains. This configuration gives you precise control over the way data is exchanged within a corporate network, for example, by limiting P2P data exchanges within a single site with the same public IP address.
Here is a simple example of what an eCDN configuration with multiple sites might look like:
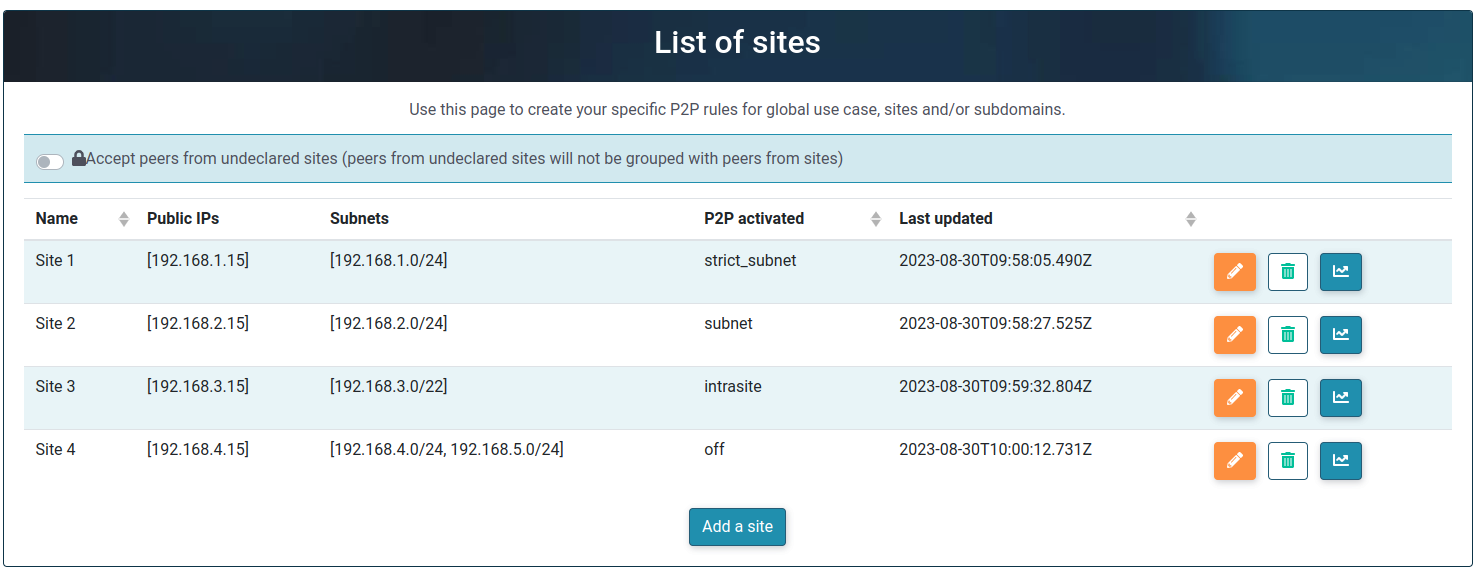
If a subnet is set, a public IP is mandatory. If you do not know the public IP, use "0.0.0.0".
In the plugin
By default, the Quanteec Plugin will not try to use the local private IP. In order to activate the local IP retrieving, an option must be added in the configuration:
let quanteecConfig = {
quanteecKey:"<enter-your-custom-videoID>",
videoID:"<enter-your-custom-videoID>",
useSubnets: true
}
Managing mDNS
By default, WebRTC uses a protocol called mDNS (multicast DNS) to hide the private IP. The protocol allows devices on the same local network to resolve hostnames (e.g., my-device.local) to IP addresses without needing a central DNS server. In WebRTC, mDNS is used to enhance privacy by hiding a user’s real local IP address from websites. Instead of exposing private IPs directly during WebRTC sessions, mDNS generates obfuscated ICE candidates (e.g., 12345.local) that are resolved to private IP addresses only within the local network.
Using mDNS in a corporate network can bring some challenges:
- The private IP are hidden, making it impossible for Quanteec to associate the peers with subnet rules.
- The network might block multicast traffic (common in enterprise networks or restrictive environments), and WebRTC peer connections may fail.
- The protocol only works within the same local network, and if users are on different subnets, the obfuscated addresses cannot be resolved.
Because of that, you might need to disable mDNS in the browser in order for the Quanteec Plugin to perform well in your environment.
When is disabling mDNS NOT needed?
Considering your network architecture, it might not be needed to disable mDNS if:
- mDNS is not blocked in the local network
- users are behind the same router
In these scenarios, the Quanteec Plugin should work just fine without any additional configuration. If at least one of the conditions is not respected, the Quanteec Plugin might fail to create connections and offload the network.
How to disable mDNS?
Disabling mDNS in the browsers depends on the browser and the OS used.
How to disable mDNS in Chrome, Chromium, and Edge
- Current Chrome, Chromium, Edge versions
- Older Chrome, Chromium, Edge versions
In Chrome-based browsers, mDNS can be disabled via the chrome flag #enable-webrtc-hide-local-ips-with-mdns.
Steps to Disable mDNS via Chrome Flags
- Open the browser (Chrome, Edge, or any Chromium-based browser).
- In the address bar, type:
chrome://flags/#enable-webrtc-hide-local-ips-with-mdns - Press Enter.
- Find the flag named " Anonymize local IPs exposed by WebRTC".
- Change the setting from Default or Enabled to Disabled.
On older versions, mDNS can be disabled by using CLI options or policies.
How to Disable mDNS in Chrome-Based Browsers Using CLI Arguments
This guide explains how to disable mDNS in Chrome-based browsers (such as Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, or Chromium) by using command-line arguments. Instructions are provided for macOS, Linux, and Windows.
- Windows
- MacOS
- Linux
Steps for Windows
- Close all instances of Chrome or the Chromium-based browser.
- Open the Command Prompt:
- Press
Win + R, typecmd, and press Enter.
- Run the following command to start Chrome with mDNS disabled:
"C:\\Program Files\\Google\\Chrome\\Application\\chrome.exe" --disable-features=WebRtcHideLocalIpsWithMdns
- If you use another Chromium-based browser, update the path to the browser`s executable.
Optional: Modify the Shortcut
To make this change permanent:
- Locate the browser shortcut on your desktop, taskbar, or start menu.
- Right-click the shortcut and select Properties.
- In the Target field, add the following to the end of the path:
–disable-features=WebRtcHideLocalIpsWithMdns. Example:“C:\Program Files\Google\Chrome\Application\chrome.exe” –disable-features=WebRtcHideLocalIpsWithMdns - Click Apply and OK.
- Use this shortcut to launch the browser with mDNS disabled.
Steps for macOS
- Open the Terminal application.
- Run the following command to launch Chrome with mDNS disabled:
/Applications/Google\\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\\ Chrome --disable-features=WebRtcHideLocalIpsWithMdns - This will start Chrome with the mDNS feature turned off, exposing local IP addresses directly in WebRTC ICE candidates.
Optional: Create a Persistent Shortcut
If you`d like to make this change permanent:
- Open the Automator app and create a new application.
- Add a "Run Shell Script" action with the following command:
/Applications/Google\\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\\ Chrome --disable-features=WebRtcHideLocalIpsWithMdns - Save the application as a custom Chrome launcher and use it to start Chrome.
Steps for Linux
- Open a terminal.
- Run the following command to launch Chrome with mDNS disabled:
google-chrome --disable-features=WebRtcHideLocalIpsWithMdns- If you
re using a different Chromium-based browser, replacegoogle-chromewith the appropriate executable name (e.g.,chromiumormicrosoft-edge`).
- If you
Optional: Modify the Application Launcher
To make this change persistent:
- Locate the
.desktopfile for your browser (usually in/usr/share/applications/or~/.local/share/applications/). - Open the
.desktopfile in a text editor. - Find the
Execline and append the following argument: `–disable-features=WebRtcHideLocalIpsWithMdns``
Example: Exec=/usr/bin/google-chrome-stable %U –disable-features=WebRtcHideLocalIpsWithMdns
- Save the file and use the application launcher to start the browser with mDNS disabled.
How to Disable mDNS in Chrome-Based Browsers Using Policies
More information about the policy can be found here: https://chromeenterprise.google/policies/#WebRtcLocalIpsAllowedUrls
- Windows
- MacOS
- Linux
Using the Group Policy Editor (For Managed Environments)
-
Download Chrome Policy Templates:
- Visit Chrome Enterprise Policy Templates and download the policy templates ZIP file.
- Extract the contents of the ZIP file.
-
Install the Policy Template:
- Copy
chrome.admxfrom thewindows/admxfolder to:C:\\Windows\\PolicyDefinitions\(policy file location).
- Copy
chrome.adml(language file) to:C:\\Windows\\PolicyDefinitions\\<your-language-code>\(e.g.,en-US).
- Copy
-
Configure the Policy:
- Open the Group Policy Editor (
gpedit.msc). - Navigate to:
Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Google -> Google Chrome -> WebRTC - Find the policy "WebRTC ICE candidate URLs for local IPs".
- Enable the policy and add the allowed URLs (one per line).
- Open the Group Policy Editor (
-
Apply the Policy:
- Run the following command in the Command Prompt to force the policy update:
gpupdate /force
- Run the following command in the Command Prompt to force the policy update:
For Local Policy (Single User)
If you do not have Group Policy Editor (e.g., on Windows Home), you can edit the registry manually:
-
Open the Registry Editor:
- Press
Win + R, typeregedit, and press Enter.
- Press
-
Navigate to the Chrome Policies Registry Key:
- For Chrome:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\Software\\Policies\\Google\\Chrome - For Edge (Chromium-based):
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\Software\\Policies\\Microsoft\\Edge
- For Chrome:
-
Create or Modify the Policy:
- Create a new String Value named
WebRTCLocalIpsAllowedUrls. - Set the value to the URLs you want to allow, separated by commas. For example:
https://example.com,https://quanteec.com
- Create a new String Value named
-
Restart the Browser:
- Relaunch Chrome or Edge for the policy to take effect.
Using a Configuration Profile on macOS (For Managed Devices)
-
Create a Configuration Profile:
- Use a tool like ProfileCreator or create a
.mobileconfigfile with the following content:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>PayloadContent</key>
<array>
<dict>
<key>PayloadType</key>
<string>com.google.Chrome</string>
<key>WebRTCLocalIpsAllowedUrls</key>
<array>
<string>https://example.com</string>
<string>https://quanteec.com</string>
</array>
</dict>
</array>
<key>PayloadType</key>
<string>Configuration</string>
<key>PayloadUUID</key>
<string>XXXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXXXXXXXXXX</string>
</dict>
</plist>
- Use a tool like ProfileCreator or create a
-
Install the Profile:
- Use an MDM tool or manually double-click the
.mobileconfigfile to install it.
- Use an MDM tool or manually double-click the
For Local Configurations
-
Open the Terminal.
-
Add a
plistconfiguration file at/Library/Managed Preferences/com.google.Chrome.plistwith the following structure:<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>WebRTCLocalIpsAllowedUrls</key>
<array>
<string>https://example.com</string>
<string>https://quanteec.com</string>
</array>
</dict>
</plist> -
Save the file and restart Chrome for the changes to take effect.
System-Wide Configuration
-
Edit or Create the Chrome Policy File:
- System-wide policies are located at:
/etc/opt/chrome/policies/managed/ - Create a JSON file, e.g.,
webrtc_policy.json:{
"WebRTCLocalIpsAllowedUrls": [
"https://example.com",
"https://quanteec.com"
]
}
- System-wide policies are located at:
-
Restart Chrome:
- Close all Chrome instances and relaunch the browser.
User-Level Configuration
-
Edit the User`s Policy File:
- User-specific policies are located at:
~/.config/chromium/managed_policies/ - Add the same JSON configuration as above.
- User-specific policies are located at:
-
Restart Chrome to apply the changes.
Mozilla Firefox
In Firefox, mDNS can be deactivated from embedded configurations.
-
Open Firefox Configuration Settings:
- Open Firefox.
- In the address bar, type:
about:config - Press Enter.
- Accept the warning message that says, "Proceed with Caution."
-
Search for the Allowed Domains Setting:
- In the search bar, type:
media.peerconnection.ice.obfuscate_host_addresses.whitelist
- In the search bar, type:
-
Modify the Setting:
- This preference allows you to specify domains for which mDNS is disabled.
- If the preference does not exist:
- Click the Add button (
+icon). - Choose String as the type.
- Enter the preference name:
media.peerconnection.ice.obfuscate_host_addresses.whitelist
- Click the Add button (
- Set its value to a comma-separated list of domains for which you want to disable mDNS:
example.com,quanteec.com - Domains must be entered without
http://orhttps://.
-
Restart Firefox:
- Close all Firefox windows and restart the browser for the changes to take effect.